Normalization and Scaling¶
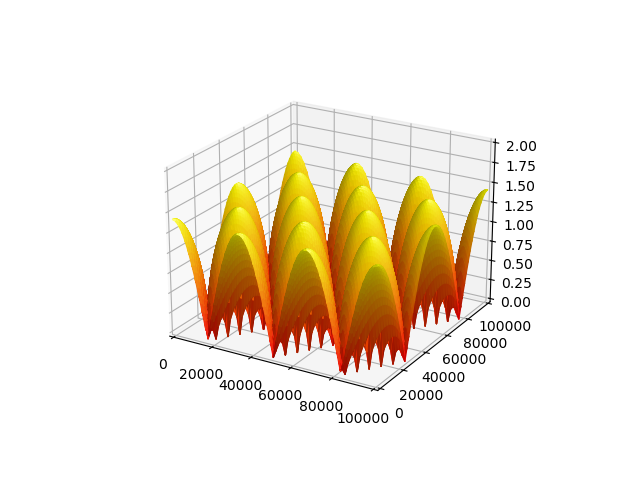
S3Dlib object defaults to a domain in the range [-1,1]. In this example, first the domain is transformed to [0,1]. The surface x and y coordinates are then scaled and then plotted in a scaled coordinate view.
This example is based on the function used in the Matplotlib example.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import s3dlib.surface as s3d
#.. Normalization and Scaling
# 1. Define functions to examine ....................................
def sincos(xyz) :
x,y,z = xyz
X, Y = 6*np.pi*x, 4*np.pi*y
Z = np.sqrt(np.abs(np.cos(X) + np.cos(Y)))
return x,y,Z
# 2. Setup and map surfaces .........................................
rez = 6
surface = s3d.PlanarSurface(rez, cmap='autumn')
# change normalization from [-1,1] to [0,1] ..........
surface.transform(scale=.5,translate=[0.5,0.5,0.5])
surface.map_geom_from_op(sincos)
surface.map_cmap_from_op( lambda xyz : xyz[2] )
surface.shade(.5).hilite(.5)
# scale the x and y coordinate directions ............
surface.transform(scale=[1e5,1e5,1])
# 3. Construct figure, add surfaces, and plot ......................
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.view_init(25)
# scale the x, y and z axes ..........................
ax.set(xlim=(0,1e5), ylim=(0,1e5), zlim=(0,2) )
ax.add_collection3d(surface)
plt.show()
