U,V Value DualCmap¶
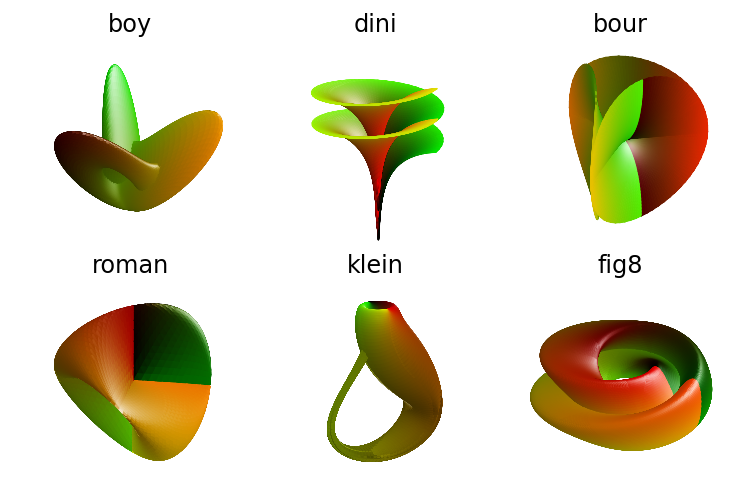
The DualCmap object is used to show the u,v parameter values in the surface:
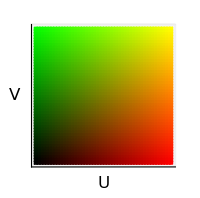
REOM: 1
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import s3dlib.surface as s3d
import s3dlib.cmap_utilities as cmu
#.. parameter u,v DualCmap colormap
# 1. Define functions to examine ...................................
def boy(xyz) :
x,y,z = xyz # u,v => x,y
u = np.pi*x/2
v = np.pi*(1+y)/2
X = (np.sqrt(2)*(np.cos(v)*np.cos(v))*np.cos(2*u) + np.cos(u)*np.sin(2*v))/(2 - np.sqrt(2)*np.sin(3*u)*np.sin(2*v))
Y = (np.sqrt(2)*(np.cos(v)*np.cos(v))*np.sin(2*u) - np.sin(u)*np.sin(2*v))/(2 - np.sqrt(2)*np.sin(3*u)*np.sin(2*v))
Z = (3*(np.cos(v)*np.cos(v)))/(2 - np.sqrt(2)*np.sin(3*u)*np.sin(2*v))
Z -= 2 # added offset for axis position.
return X,Y,Z
def dini(rtz) :
r,t,z = rtz # u,v => t,r
a, b = 1, 0.2
T = 2*t
x = a*np.cos(T)*np.sin(r)
y = a*np.sin(T)*np.sin(r)
z = a*(np.cos(r) + np.log(np.tan(r/2))) + b*T
return x,y, 0.333*z # note: scale.z
def bour(rtz) :
r,t,z = rtz # u,v => r,t
T = 2*t
x = r*np.cos(T) - np.power(r,2.0)*np.cos(2*T)/2.0
y = -r*np.sin(T) * ( r*np.cos(T) + 1.0)
z = 1.3333*np.power(r,1.5)*np.cos(1.5*T)
return x,y,z
def roman(rtp) :
r,t,p = rtp # u,v => t,p
ct, st = np.cos(t), np.sin(t)
cp, sp = np.cos(p), np.sin(p)
cp_sp = cp*sp
ct_st = ct*st
x = cp*ct_st
y = sp*ct_st
z = cp_sp*np.square(ct)
return x,y,z
def klein(rtp) :
r,t,p = rtp # u,v => p,t
u = p
v = t
cU, sU = np.cos(u), np.sin(u)
cV, sV = np.cos(v), np.sin(v)
x = -(2/15)*cU* \
( ( 3 )*cV + \
( -30 + 90*np.power(cU,4) - 60*np.power(cU,6) + 5*cU*cV )*sU \
)
y = -(1/15)*sU* \
( ( 3 - 3*np.power(cU,2) -48*np.power(cU,4) +48*np.power(cU,6) )*cV + \
(-60 + ( 5*cU - 5*np.power(cU,3) - 80*np.power(cU,5) + 80*np.power(cU,7) )*cV )*sU \
)
z = (2/15)*( 3 + 5*cU*sU )*sV
return x,y,z
def fig8(rtp) :
r,t,p = rtp # u,v => t,p
v = 2*p
R=2
Q = ( R + np.cos(t/2)*np.sin(v) - np.sin(t/2)*np.sin(2*v) )
x = Q*np.cos(t)
y = Q*np.sin(t)
z = np.sin(t/2)*np.sin(v) + np.cos(t/2)*np.sin(2*v)
return x,y,z
# 2. Setup and map surface .........................................
rez = 6
kr = cmu.hsv_cmap_gradient( [0.00,1,0], [0.00,1,1],name='black_red' )
kg = cmu.hsv_cmap_gradient( [0.33,1,0], [0.33,1,1],name='black_green' )
cmap2d = cmu.DualCmap(kr,kg)
boyS = s3d.PlanarSurface(rez, basetype='oct1')
boyuv = lambda xyz : cmap2d(xyz[0],xyz[1])
diniS = s3d.PolarSurface(rez-1, basetype='hex_c', minrad=0.01)
diniuv = lambda rtz : cmap2d(rtz[1],rtz[0])
bourS = s3d.PolarSurface(rez, basetype='hex_c')
bouruv = lambda rtz : cmap2d(rtz[0],rtz[1])
romanS = s3d.SphericalSurface(rez-1,basetype='octa_c',minrad=0.01)
romanuv = lambda rtp : cmap2d(rtp[1],rtp[2])
kleinS = s3d.SphericalSurface(rez,basetype='octa_c',minrad=0.01)
kleinuv = lambda rtp : cmap2d(rtp[2],rtp[1])
fig8S = s3d.SphericalSurface(rez,basetype='octa_c')
fig8uv = lambda rtp : cmap2d(rtp[1],rtp[2])
surfaces = [ boyS, diniS, bourS, romanS, kleinS, fig8S ]
geomFunc = [ boy, dini, bour, roman, klein, fig8 ]
colorLam = [ boyuv, diniuv, bouruv, romanuv, kleinuv, fig8uv ]
elevazim = [ None, [20,-60], [30,-40], [20,-80], [20,-125], [35,-60] ]
minmaxAr = [ [-1.4,1.4], [-0.75,.75], [-1,1], [-.375,.375], [-1.5,1.5], [-2,2] ]
# 3. Construct figure, add surface plot ............................
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7.5,5))
for i,surface in enumerate(surfaces) :
ax = fig.add_subplot(231+i, projection='3d', aspect='equal')
ax.set_axis_off()
minmax, elaz = minmaxAr[i], elevazim[i]
ax.set(xlim=minmax, ylim=minmax, zlim=minmax)
if elaz is not None : ax.view_init(*elaz)
geomF, colorUV = geomFunc[i], colorLam[i]
surface.map_geom_from_op( geomF, returnxyz=True )
surface.map_color_from_op( colorUV )
if i==4 : surface.transform(s3d.eulerRot(0,-90),translate=[0,0,2])
ax.set_title(surface.name , fontsize='xx-large')
ax.add_collection3d(surface.shade(.5,ax=ax).hilite(0.8,focus=1.5,ax=ax))
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
