Radial Color Mapped¶
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator
import s3dlib.surface as s3d
#.. Radial Color Mapped
# 1. Define functions to examine ....................................
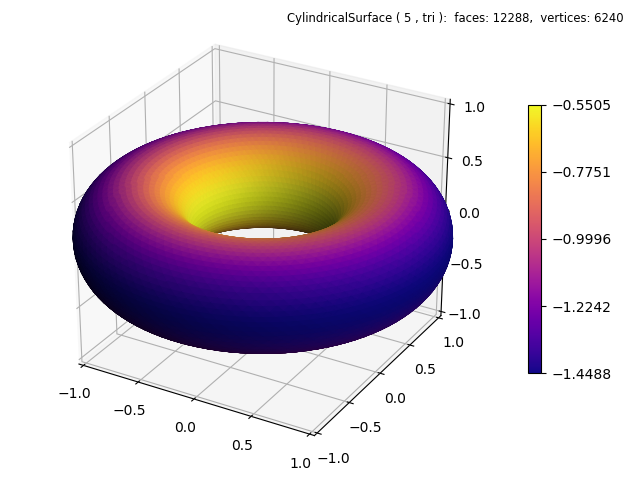
def torusFunc(rtz) :
r,t,z = rtz
ratio = .45
Z = ratio*np.sin(z*np.pi)
R = r + ratio*np.cos(z*np.pi)
return R,t,Z
# 2. Setup and map surfaces .........................................
rez=5
torus = s3d.CylindricalSurface(rez).map_geom_from_op( torusFunc )
torus.map_cmap_from_op( lambda xyz : -xyz[0], 'plasma')
# 3. Construct figure, add surfaces, and plot ......................
fig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(0.75))
fig.text(0.975,0.975,str(torus), ha='right', va='top', fontsize='smaller', multialignment='right')
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.set(xlim=(-1,1), ylim=(-1,1), zlim=(-1,1) )
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(5))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(5))
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(5))
minc = torus.bounds['vlim'][0]
maxc = torus.bounds['vlim'][1]
plt.colorbar(torus.cBar_ScalarMappable, ax=ax, ticks=np.linspace(minc,maxc,5), shrink=0.6 )
ax.add_collection3d(torus.shade())
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Note
In the highlighted line, the lambda function uses the negative of the radial coordinate for color mapping. This effectively uses a color map that is reversed.
