SliceSet Geometry and Color¶
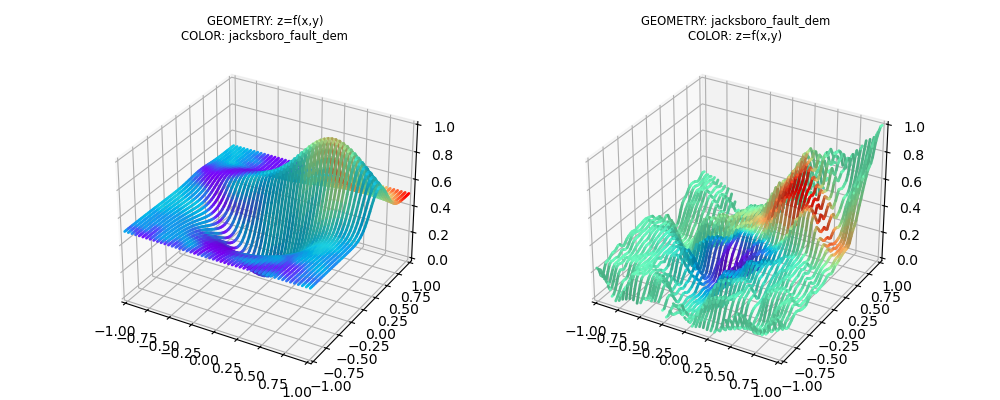
This example demonstrates that two scalars, which are dependent on x and y coordinates, can both be represented as a single 3D surface. One scalar used for geometry and the other scalar used for color.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import s3dlib.surface as s3d
#.. SliceSet geom & color from func & datagrid
# 1. Define function to examine .....................................
z=np.load('data/jacksboro_fault_dem.npz')['elevation']
datagrid = np.flip( z[5:50, 5:50], 0 )
def parFunXY(xyz):
x,y,z = xyz
X,Y = 3*x, 3*y
Z1 = np.exp(-(X**2 + Y**2) / 2) / (2 * np.pi)
Z2 = (np.exp(-(((X - 1) / 1.5)**2 + ((Y - 1) / 0.5)**2) / 2) /
(2 * np.pi * 0.5 * 1.5))
Z = Z2 - Z1
Z = 3*Z + 0.5
return x,y,Z
def func_Z(xyz) : return parFunXY(xyz)[2]
# 2. Setup and map lines .........................................
rez, numSlices, lw = 5, 50, 2
cmap = 'rainbow'
line1 = s3d.ParametricLine(rez, name='GEOMETRY: z=f(x,y)', lw=lw )
line1.map_xySlice_from_op( parFunXY, xset=numSlices)
line1.map_cmap_from_datagrid( datagrid, cmap, cname='COLOR: jacksboro_fault_dem')
line2 = s3d.ParametricLine(rez, name='GEOMETRY: jacksboro_fault_dem', lw=lw)
line2.map_xySlice_from_datagrid(datagrid, xset=numSlices)
line2.map_cmap_from_op( func_Z, cmap, cname='COLOR: z=f(x,y)' )
# 3. Construct figure, add surface, plot ............................
lines = [ line1, line2 ]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
for i,line in enumerate(lines) :
ax = fig.add_subplot(121+i, projection='3d')
ax.set(xlim=(-1,1), ylim=(-1,1), zlim=(0,1) )
title = line.name + '\n' + line.cname
ax.set_title(title, fontsize='small')
ax.add_collection3d(line.shade(0.5))
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
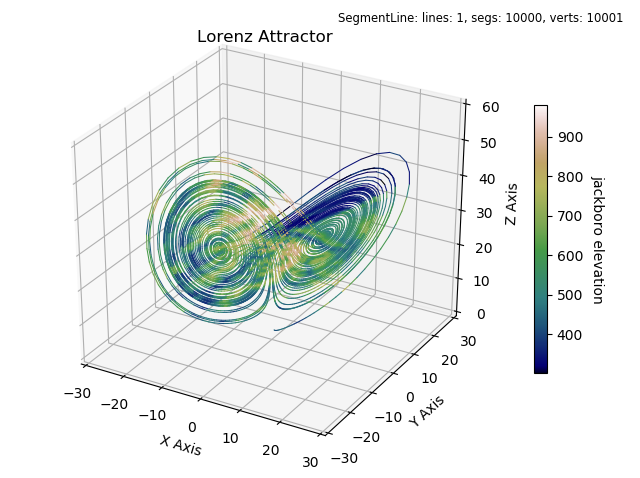
The above plot uses a ParametricLine object, however this may be applied to any line object. For example, the following figure uses the Lorenz Attractor segmented line with coloring from the datagrid.